As novel types of Biologics have been developed, changes in biomanufacturing approaches have been running in parallel with the intention of maximising yield and lowering production costs. Evolution Global have identified 8 key production trends that will shape the Future of BioManufacturing, the second of which is Modular Factories.
The Future of BioManufacturing: Modular Factories & End-to-End Solutions
INTRODUCTION
Modular factories comprise multiple, prefabricated and easy-to assemble component sections, designed to offer a highly-flexible, simple and cost-effective solution for creating production sites. In the context of biomanufacturing, modular factories can be defined as a prefabricated cGMP biomanufacturing facilities.
The modules themselves can be constructed off-site and then transported to the installation site entirely (or mostly) complete and then assembled in situ. Alternatively, large-scale “BioPark” complexes can house customisable modular facilities for multiple companies and processes in a centralised location.
THE MODULAR FACTORY MARKET
EXPLORING THE STRATEGIES OF LONZA, GE HEALTHCARE & MERCK
The Modular Biomanufacturing Factory sector is in early stages of development and, at present, Lonza, GE Healthcare & Merck (MilliporeSigma & BioReliance) are the core players within this space.
Our timeline below outlines the recent events that have shaped the development of modular biomanufacturing facilities:
GE HEALTHCARE’S KUBio
GE’s KUBio facilities are based on housing single-use technology for rapid switching between processes and include all necessary infrastructure components such as clean rooms, piping and HVAC systems, designed to meet FDA and EMA GMP standards. It should be noted that GE also develops modular solutions in the Oil & Gas (Small-Scale Liquefied Natural Gas [LNG] Plants), Desalination, and Small to Medium Nuclear power sectors (SMR). This knowledge is likely to have added value to the KUBio concept, which can be stated to have started in 2012 as a bona fide offering to the market.
The exemplar project that GE leveraged in order to springboard KUBio was the construction of a facility for JHL Biotech, a multinational biopharmaceutical company with operations in China. The KUBio plant, shipped to China from Sweden, Germany & the United States in 62 modules, was assembled in Wuhan in 11 days. From a footprint perspective, whilst not published in detail, it is likely that the Wuhan site offers a compact footprint of approximately 1,200m2 with a total area of 2,200m2 split on two levels.
From an operational perspective, the JHL Biotech KUBio facility contains 4 x 2,000L single-use bioreactors. This is quite serious market quantity capacity considering that over the last decade, improvements in commercial production of monoclonal antibodies and other proteins has seen up to 10-fold increases in titres. A 2,000L disposable bioreactor can conceivably replace a 20,000L stainless-steel vessel, but more likely it is in the region of 10,000L stainless steel vessel. Based on these estimations the Wuhan site has a theoretical capacity of 40,000L, which can be directed towards single product manufacture or towards 4 different products.
In April 2018 GE launched the KUBio BSL2, which is specifically designed to manufacture viral vector-based therapeutics, including viral vector-based vaccines, oncolytic viruses and gene and cell therapies that require a biosafety level 2 (BSL2) production environment. Mats Lundgren, Customer Application Director at GE Healthcare Life Sciences, notes that “the viral vector-based therapy market is expected to grow rapidly and currently there are over 700 viral vector-based therapies in clinical trials.”
Since KUBio was launched, GE Healthcare reports that the company has brought three KUBio’s to China, as well as over 50 FlexFactories to the market globally. BeiGene, which already utilises GE’s FlexFactory technology in its Suzhou manufacturing plant, recently announced that its Guangzhou-based KUBio facility for cancer monoclonal antibodies will become operational in 2019. Additionally, GE claims that the company is currently in talks with several potential customers for its new KUBio BSL2 factories.
LONZA’S IBEX SOLUTIONS
Lonza’s Ibex Solutions offer drug developers agile facilities that span the preclinical to commercial stages, from drug substance development and manufacture to drug product manufacture. Lonza states that its new modular complex is expected to shorten customers’ time to market by 12 months or more. Additional benefits include flexibility to manage uncertainty, supply chain simplification, reduced capital expenditure and risk management across the entire product life-cycle.
The Ibex biomanufacturing complex is integrated into Lonza’s 100,000m2 BioPark facility in Visp, Switzerland, thereby leveraging the company’s existing infrastructure, support networks and highly skilled workforce. The facility has been designed flexibly to give customers complete freedom in facility design and implementation and the ability to respond rapidly as needs evolve.
Lonza’s Ibex Solutions consist of three offerings, which together offer complete product life-cycle management in one central site:
- Ibex Design: covers the early stages of creating a new biologic, from gene through to clinical phase I. The offering comprises a pioneering fixed-price gene-to-vial package with terms under which Lonza will deliver drug product based on at least 1 kg drug substance within 12 months. The package also includes the reservation of a manufacturing slot for clinical resupply.
- Ibex Develop: helps companies seamlessly and rapidly transition from clinical phase II to commercialization. The offering enables biologics license applications (BLAs) to be submitted within 22 months from the start of process characterization. Eliminating the need for tech transfers, allowing process optimizations and creating operational efficiencies are expected to accelerate the path to market.
- Ibex Dedicate: A modular, technology-agnostic biomanufacturing concept with reduced CAPEX and accelerated timelines, enabling speed to market or allowing biopharma companies to delay investment decisions to decrease financial risk.
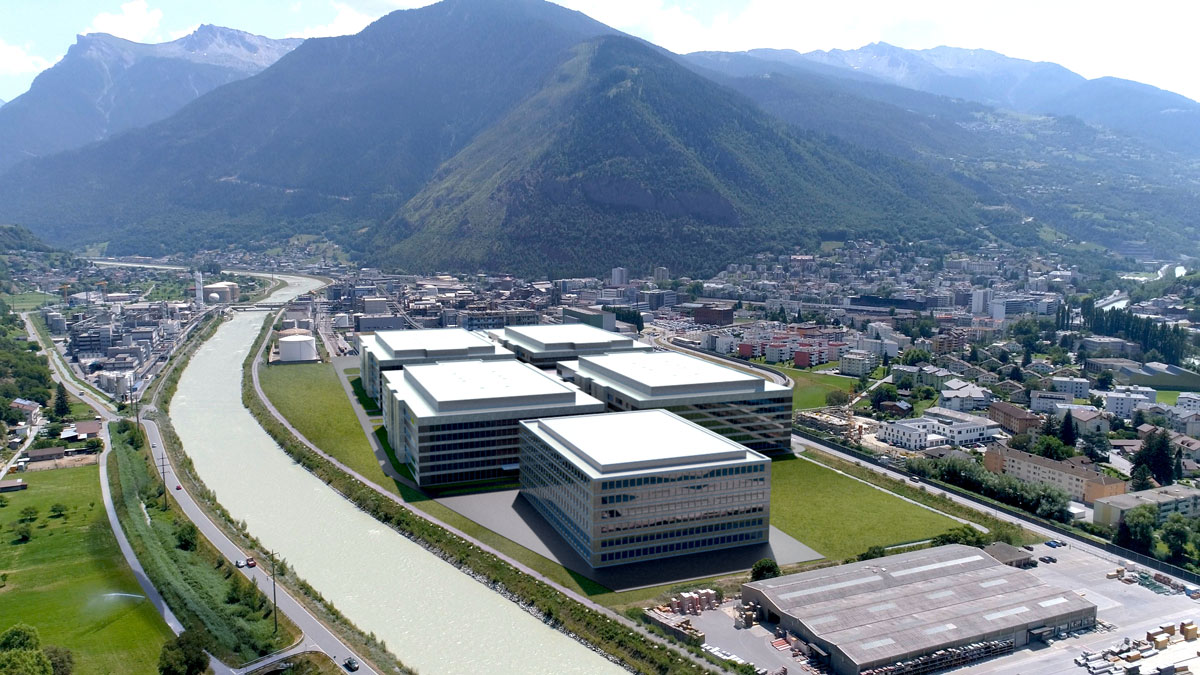

The Ibex Solutions takes advantage of Lonza’s proven platform technologies, such as the GS Gene Expression System and the company’s expertise in drug product development. The application of single-use technologies and a high degree of automation further increase the efficiency of the Ibex Solutions. In addition, customers of all three Ibex™ Solutions can benefit from the ability to scale-up or scale-out to other sites in the established Lonza network in Europe, America or Asia.
This approach is markedly different from that of GE, which instead opted to partner with external engineering company M+W Group to build modules which are then shipped to the final factory location. GE Healthcare have adopted a similar strategy to Lonza’s Visp facility, with the construction of a €150M GE BioPark in Cork, Ireland expected to be complete by the end of 2018.
The first facility developed at the Ibex Solutions BioPark is a large-scale mammalian cell culture facility for the production of monoclonal antibodies, jointly funded by Lonza and Sanofi. Whilst Ibex Dedicate facilities are already active at the Visp site, Ibex Design and Ibex Develop facilities are currently under construction and are expected to become operational from 2020.
MERCK’S PROVANTAGE END-TO-END SOLUTIONS
Merck’s Provantage End-to-End solution is a comprehensive suite of products and services enabling biopharmaceutical companies to accelerate the progression of molecules into the clinic and toward commercialization. The turnkey package includes process development, cGMP manufacturing, facility design, equipment for pilot plant production, process and equipment training, technology transfer, equipment qualification and set-up for commercialization.
Merck provides a dedicated Project Manager responsible for leading an experienced team of process development and biologics production experts. The Project Manager then oversees the implementation of Merck’s Provantage End-to-End services, which are split across five stages:
- Process Development: Enables drug developers to reduce the time required to develop and produce cGMP biomolecules for clinical trials.
- ClinicReady Template: BioReliance ClinicReady template for mAbs provides drug developers with configurable Upstream and Downstream single-use production equipment for mAbs adapted to cGMP production of pre-clinical, Phase I, II and III material.
- GMP Clinical Supply Solutions: Unlike other CMOs, Merck’s Biodevelopment Center enables open source manufacturing by providing access to state of the art GMP production capabilities with the full freedom and transparency needed to define bespoke production strategies.
- Tech Transfer Services: The goal of technology transfer activities is to transfer product and process knowledge from development and GMP clinical production to GMP commercial manufacturing location. Merck offers tech transfer services that enable drug developers to efficiently transfer to local manufacturing partners or novel facilities.
- Facility Design & Construction: Merck works closely with leading modular cleanrooms and facility engineering and construction companies to build bespoke, agile and flexible biopharmaceutical factories.
WHY GO MODULAR?
Ultimately the attraction of implementing modular biomanufacturing facilities is financial. Traditional bricks-and-mortar large-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing facilities typically cost $200 to $500 million. It should be noted that this is significantly more than the $30 to $100 million for similar-scale, small-molecule plants. In both cases, it takes four to five years, from breaking ground to completion.
By contrast, a KUBio facility costs 25% to 50% less than building a traditional plant, offering drug manufacturers assembled, qualified and ready-to-run capacity within 14 to 18 months. Additionally, KUBio facilities are significantly less harmful to the environment, reducing CO2 emissions by 75% and water and energy use by 80%, largely because of the greatly reduced requirement for cleaning and sterilising stainless steel components. The implementation of single-use technologies within KUBio facilities offers ongoing cost reductions, however it should be noted that these calculations do not fully consider the costs of plastic disposal.
Lonza’s Ibex Solutions and Merck’s Provantage End-to-End solutions do not offer the same location flexibility as GE’s KUBio, which can be shipped globally. Lonza has instead opted to centralise their modular factory facilities in its state-of-the-art BioPark in Visp, thereby enabling the company offer its clients a more holistic and streamlined approach to drug development. Merck offers similar streamlined End-to-End services out of its many global facilities, however when it comes to modular factories the company relies on external engineering and construction partners rather than keeping it all in-house.
Merck places a high value on technology transfer and promotes its Provantage End-to-End services as open-source manufacturing, which provides greater freedom and flexibility for clients to transfer an established process to alternative facilities. Merck gives clients access to its GMP production capabilities with “full freedom and transparency” to transfer the process to external facilities without any royalties.
TARGET MARKETS
It’s likely that the primary market for modular biopharmaceutical factories are regions that will be ramping up the requirement for biologics and who seek to retain a portion of the expenditure associated with biologics within the economy, for either economic or regulatory reasons. As such, the emerging markets are the most likely targets for the modular biomanufacturing approach.
From the Asia Pacific perspective, IMS Health projects that China will be the second largest market for Biologics by 2020. Current development activity is significant: as of May 2017, China had 171 monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapeutics under clinical development from 82 different biologics manufacturers. In 2016 alone, 32 new projects entered clinical trials.
2017 BIOLOGICS RANKINGS
| REGION | MANUFACTURING (% OF GLOBAL CAPACITY) | MARKET SHARE (REVENUE) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 1 (36%) | 1 (46%) |
| Europe | 2 (24%) | 2 (22%) |
| China | 4 (8%) | 4 (9%) |
2020 BIOLOGICS RANKINGS
| REGION | MANUFACTURING (% OF GLOBAL CAPACITY) | MARKET SHARE (REVENUE) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 1 (36%) | 1 (46%) |
| China | 2 (22%) | 2 (24%) |
| Europe | 3 (20%) | 3 (20%) |
China now boasts the second-highest number of biosimilars in development after the United States, as highlighted by estimates that 27 companies are currently developing a biosimilar to Humira (adalimumab). Alphamab, a Suzhou, China–based biologics drug company, claims to have 28 biosimilar programs in development, followed by Qilu Pharmaceuticals with 10 active programs. There is a clear gap in the Chinese biomanufacturing requirement, which is highlighted by the fact the concentration of global biopharmaceutical manufacturing is heavily skewed towards the US and European Markets.
Additionally, the market for viral vector-based therapies continues to grow globally, with over 700 active therapies in clinical development. Merck, Lonza and GE Healthcare are all strategically positioned to take advantage of the growing gene therapy market in the coming years.
CONCLUSION
It should be noted that modular biomanufacturing is likely to be the domain of markets/geographies that require facilities quickly and have pressing market needs. In the developed west, there is less of a requirement for modular factories, as there are a significant number of active legacy biomanufacturing sites that include both Direct and Contract Biologic Manufacture. Most have been based on Stainless Steel, but have incorporated many aspects of single use including extra capacity especially for pilot and clinical trial scale.
There are concerns that such facilities were for designed for lower-titre quantities of product using what can be perceived as first-generation technology, and as such are no longer cost-effective. However it is important to note that whilst in general titres have improved, larger scales may be still required for certain products that are particularly challenging such as toxic proteins.
In the context of a modular factory approach in Western markets, it is unlikely that modules will be required, as internal bricks-and-mortar sites will likely be re-configured to accommodate greater utilisation of single-use technologies for small-scale market quantities, provided that it is economically viable to do so. This is the strategy that is currently being progressed by both Merck and Lonza, with both companies attempting to differentiate their services from those of GE Healthcare by offering additional biopharmaceutical expertise and a streamlined process that encompasses the entire drug development and commercialisation process.
Please use the buttons below to navigate through Evolution Global’s “Future of BioManufacturing” series. The next key trend examines the impact of Reductions in Market Scale Quantities.
EVOLUTION BIOSCIENCE WILL HELP YOUR BUSINESS FLOURISH












